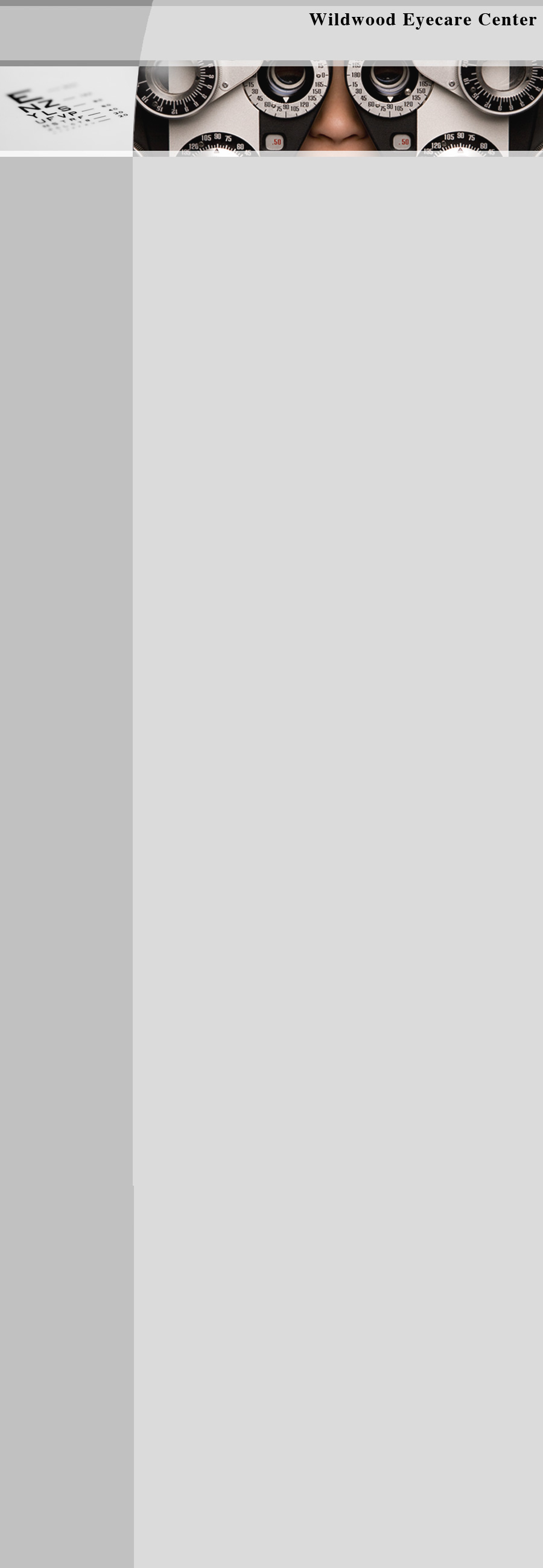Patient History
A patient history helps to determine any symptoms the individual is experiencing, when they began, the presence of any general health problems, medications taken and occupational or environmental conditions that may be affecting vision. The doctor will ask about any eye or vision problems you may be having and about your overall health.
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity measurements evaluate how clearly each eye is seeing. As part of the testing, you are asked to read letters on distance and near reading charts. The results of this testing are written as a fraction with 20/20 being normal distance visual acuity.
Preliminary Tests
Preliminary testing may include evaluation of specific aspects of visual function and eye health such as depth perception, color vision, eye muscle movements, peripheral or side vision, and the way your pupils respond to light.
Keratometry
This test measures the curvature of the cornea, the clear outer surface of the eye, by focusing a circle of light on the cornea and measuring its reflection. This measurement is particularly critical in determining the proper fit for contact lenses.
Refraction
Refraction is conducted to determine the appropriate lens power needed to compensate for any  refractive error (nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism). The doctor will use an automated instrument to automatically evaluate the focusing power of the eye. The power is then refined by patient's responses to determine the lenses that allow the clearest, sharpest vision possible.
refractive error (nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism). The doctor will use an automated instrument to automatically evaluate the focusing power of the eye. The power is then refined by patient's responses to determine the lenses that allow the clearest, sharpest vision possible.
Eye Focusing, Eye Teaming, and Eye Movement Testing
Assessment of accommodation, ocular motility and binocular vision determines how well the eyes focus, move and work together. In order to obtain a clear, single image of what is being viewed, the eyes must effectively change focus, move and work in unison. This testing will look for problems that keep your eyes from focusing effectively.
Eye Health Evaluation
External examination of the eye includes evaluation of the cornea, eyelids, conjunctiva and surrounding eye tissue using a biomicroscope.
Evaluation of the lens, retina and posterior section of the eye may be done through a dilated pupil or dilated retinal scanning to provide a better view of the internal structures of the eye.
The Nikon California Optomap digital retinal imaging device captures
more than 80% of your retina in one image. Traditional methods typically
reveal only 10-45% of your retina at one time. The unique optomap
ultra-widefield view enhances your eye doctor's ability to detect even the
earliest sign of disease that appears on your retina. Seeing most of the retina
at once allows your eye doctor more time to review your images and educate
you about you eye health.
Measurement of this fluid pressure within the eye (tonometry) is performed.
These measurements help to determine the risk of developing glaucoma.
Supplemental testing
Additional testing may be needed based on the results of the previous tests
to confirm or rule out possible problems, to clarify uncertain findings, or to
provide a more in-depth assessment.
At the completion of the examination, your doctor will assess and evaluate
the results of the testing to determine a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan.
He will discuss with you the nature of any visual or eye health problems found
and explain available treatment options.
If you have questions regarding any eye or vision conditions diagnosed, or treatment recommended, don't hesitate to ask for additional information or explanation from your doctor.
Periodic eye and vision examinations are an important part of preventive health care. Many eye and vision problems have no obvious signs or symptoms. As a result, individuals are often unaware that problems exist. Early diagnosis and treatment of eye and vision problems are important in maintaining good vision and eye health, and when possible, preventing vision loss.
A comprehensive adult eye and vision examination may include, but is not limited to, the following tests. Individual patient signs and symptoms, along with the professional judgment of the doctor, may significantly influence the testing done.
Eye Examinations:
Comprehensive Eye Examination
Contact Lens Examination
School-Age Children Examinations
Contact lens examinations include special tests that are not preformed during a routine comprehensive eye examination.
An estimated 17-25% of school children have vision problems. Many of these problems interfere with a child’s ability to reach his or her potential in school. The American Optometric Association recommends eye examinations by 6 months old, at 3 years old, before 1st grade, and every 2 years until age 18.
1st time contact lens wearers will incur an evaluation fee that includes:
Annual recheck appointments will be necessary in conjunction with your comprehensive eye exam to ensure your corneal health, while wearing contact lenses, and to update your contact lens prescription.
Take notice if your child:
Get help if your child:
Remember, many eye problems have no symptoms. Professional care is the only way to detect some problems. Early treatment is the most effective. Call us today to schedule a comprehensive eye examination for your child.
Donald J. Beilstein, O.D.
Mujahid A. Hines, M.D.
11250 Pleasant Valley Road
Penn Valley California 95946
Phone: 530 . 432 . 2020